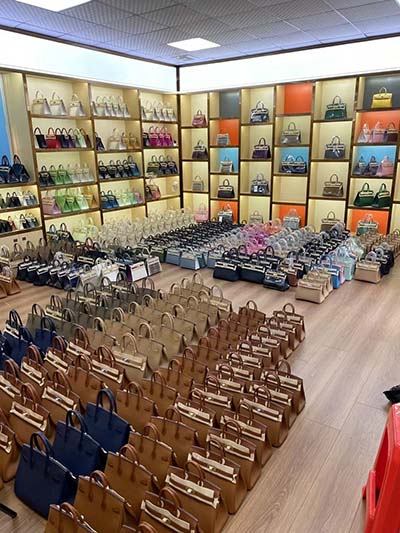
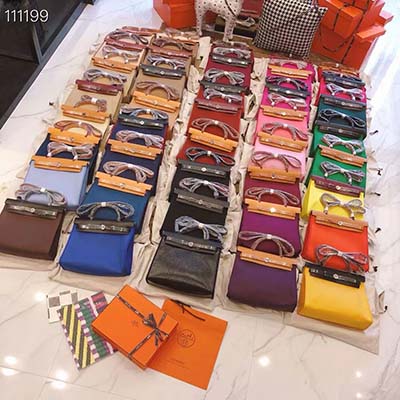
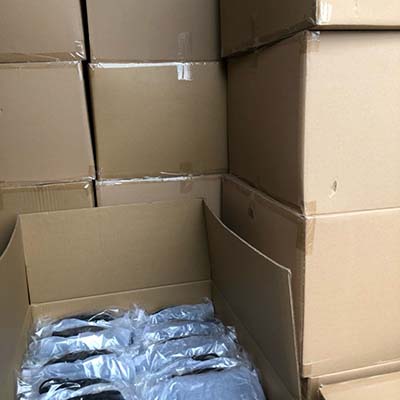
platos hermes | hermes plato platos hermes Unique plates, mugs, bowls or dinner set molded with finesse. Tea and coffee service, bowls or decorative pieces made with refinement in our Hermès online store. $33.75
0 · plato's protagoras hermes
1 · hermes tableware
2 · hermes propylaeus wikipedia
3 · hermes plato
4 · hermes in ancient greece
5 · hermes dishes for sale
6 · hermes dinnerware sets
7 · hermes characteristics wikipedia
$110.00
plato's protagoras hermes
Hermes is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, merchants, and orators. He is able to move quickly and freely between the worlds of the mortal and the divine aided by his winged sandals. Hermes plays the role of the psychopomp or "soul guide"—a conductor of souls into the afterlife.
hermes tableware
What About Hermes? A Reconsideration of the Myth of Prometheus in Plato's Protagoras* SERGIO YONA ABSTRACT: This essay reevaluates scholarship regarding the myth of .Unique plates, mugs, bowls or dinner set molded with finesse. Tea and coffee service, bowls or decorative pieces made with refinement in our Hermès online store.
A collection of studies on the interaction of Hermetic and Platonic influences throughout the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period.Hermes was the ancient Greek god of herds and flocks, travellers and hospitality, roads and trade, thievery and cunning, heralds and diplomacy, language and writing, athletic contests and gymnasiums. He was also the herald Zeus, king of the gods. This essay reevaluates scholarship regarding the myth of Prometheus in Plato’s Protagoras and offers a new interpretation that focuses on the potential of Hermes as .
This article examines how Plato uses mythological symbolisms in the Lysis, specifically those of Hermes, to show how our experience of the good makes possible our .
Hermes (Greek: Ἑρμής, transl.: Hermés) was, in Greek mythology, one of the Olympian gods, son of Zeus and Maia, and possessor of several attributes.In the light of one of the dialogue’s central etymological accounts – Socrates’ etymology of the name Hermes – this paper discusses two recent and influential versions of such a view: David .
hermes propylaeus wikipedia
hermes plato
versace yellow diamond for men
Hermes was the Olympian god of herds, trade, heralds, athletes and thieves. This page contains stories of Hermes from the sagas of the gods including his slaying of the hundred-eyed giant Argos Panoptes, his role in the War of the Giants, flight from the monster Typhoeus, participation in the creation of Pandora, the birth of his son Pan, his .
Hermes (/ ˈ h ɜːr m iː z /; ‹See Tfd› Greek: Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, [2] merchants, and orators.
What About Hermes? A Reconsideration of the Myth of Prometheus in Plato's Protagoras* SERGIO YONA ABSTRACT: This essay reevaluates scholarship regarding the myth of Prometheus in Plato's Protagoras and offers a new interpretation that focuses on the potential of Hermes as representative par exUnique plates, mugs, bowls or dinner set molded with finesse. Tea and coffee service, bowls or decorative pieces made with refinement in our Hermès online store.
A collection of studies on the interaction of Hermetic and Platonic influences throughout the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period.Hermes was the ancient Greek god of herds and flocks, travellers and hospitality, roads and trade, thievery and cunning, heralds and diplomacy, language and writing, athletic contests and gymnasiums. He was also the herald Zeus, king of the gods.
Hermes (Greek: Ἑρμής, transl.: Hermés) was, in Greek mythology, one of the Olympian gods, son of Zeus and Maia, and possessor of several attributes.Hermes was the Olympian god of herds, trade, heralds, athletes and thieves. This page contains stories of Hermes from the sagas of the gods including his slaying of the hundred-eyed giant Argos Panoptes, his role in the War of the Giants, flight from the monster Typhoeus, participation in the creation of Pandora, the birth of his son Pan, his . This essay reevaluates scholarship regarding the myth of Prometheus in Plato’s Protagoras and offers a new interpretation that focuses on the potential of Hermes as representative par excellence of the Protagorean, or, more generally, sophistic tradition.
In the light of one of the dialogue’s central etymological accounts – Socrates’ etymology of the name Hermes – this paper discusses two recent and influential versions of such a view: David Sedley’s theory of onomatopoetic encapsulation and Franco Trivigno’s qualified referentialism. This article examines how Plato uses mythological symbolisms in the Lysis, specifically those of Hermes, to show how our experience of the good makes possible our capacity to love our friend as an individual, and in so doing overturns the static dualities usually associated with Plato’s ‘metaphysics’.Hermes (/ ˈ h ɜːr m iː z /; ‹See Tfd› Greek: Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology considered the herald of the gods. He is also widely considered the protector of human heralds, travelers, thieves, [2] merchants, and orators.
What About Hermes? A Reconsideration of the Myth of Prometheus in Plato's Protagoras* SERGIO YONA ABSTRACT: This essay reevaluates scholarship regarding the myth of Prometheus in Plato's Protagoras and offers a new interpretation that focuses on the potential of Hermes as representative par exUnique plates, mugs, bowls or dinner set molded with finesse. Tea and coffee service, bowls or decorative pieces made with refinement in our Hermès online store. A collection of studies on the interaction of Hermetic and Platonic influences throughout the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period.
Hermes was the ancient Greek god of herds and flocks, travellers and hospitality, roads and trade, thievery and cunning, heralds and diplomacy, language and writing, athletic contests and gymnasiums. He was also the herald Zeus, king of the gods.

Hermes (Greek: Ἑρμής, transl.: Hermés) was, in Greek mythology, one of the Olympian gods, son of Zeus and Maia, and possessor of several attributes.
Hermes was the Olympian god of herds, trade, heralds, athletes and thieves. This page contains stories of Hermes from the sagas of the gods including his slaying of the hundred-eyed giant Argos Panoptes, his role in the War of the Giants, flight from the monster Typhoeus, participation in the creation of Pandora, the birth of his son Pan, his . This essay reevaluates scholarship regarding the myth of Prometheus in Plato’s Protagoras and offers a new interpretation that focuses on the potential of Hermes as representative par excellence of the Protagorean, or, more generally, sophistic tradition.
In the light of one of the dialogue’s central etymological accounts – Socrates’ etymology of the name Hermes – this paper discusses two recent and influential versions of such a view: David Sedley’s theory of onomatopoetic encapsulation and Franco Trivigno’s qualified referentialism.
hermes in ancient greece
hermes dishes for sale
$40.00
platos hermes|hermes plato